Outdoor Environment
Outdoor installation usually has the following characteristics.
-
The device is installed outdoors with a lightning protection system or a higher building nearby.
-
The cables are routed over a long distance.
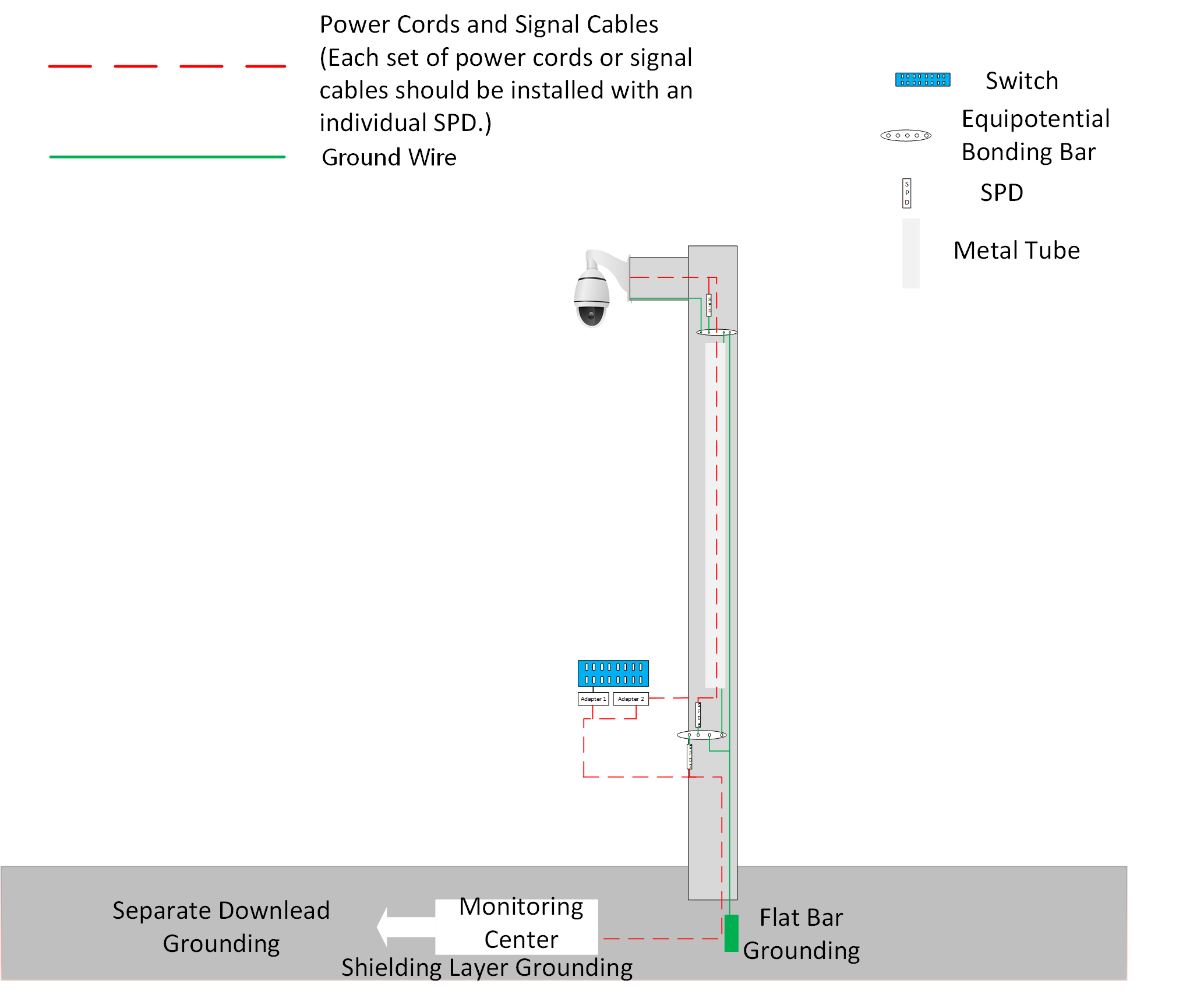
When the device is installed outdoors and within the protective radius of a lightning protection system or a higher building nearby, it is not likely to be struck directly but has a higher risk to be struck indirectly. Different types of lightning hazards in outdoor environments and solutions are as follows.
|
Type |
Description |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
Ground Potential Rise |
When a nearby object is hit directly by lightning and the resistance on its releasing path is too high, if the device and the object have the common ground, the transient current and high voltage will go into the device through the ground wire and cause damage. |
Ground the device separately. Avoid common ground with the lightning protection system. |
|
Lightning Electromagnetic Pulse |
In an open field, the electromagnetic pulse caused by electric discharge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to ground couples into the wires of the device through space and causes damage. |
It is usually required to enclose device cables with shielded metal pipes and ground the metal pipes. Long-distance cables are required to be buried underground. Overhead wiring is not allowed. Every line into the device should be installed with SPD. |
|
Surge Energy |
When the cable runs over a long distance, the surge energy from the far end also poses high risk. |